IBM cloud computing course

international Business Machines (IBM), is a global technology company that provides hardware, software, cloud-based services and cognitive computing. it was originally called Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company. It would be renamed to IBM in 1924. Given that the company is over 100 years old it is no surprise that it has had to adjust to different technological trends throughout the decades.
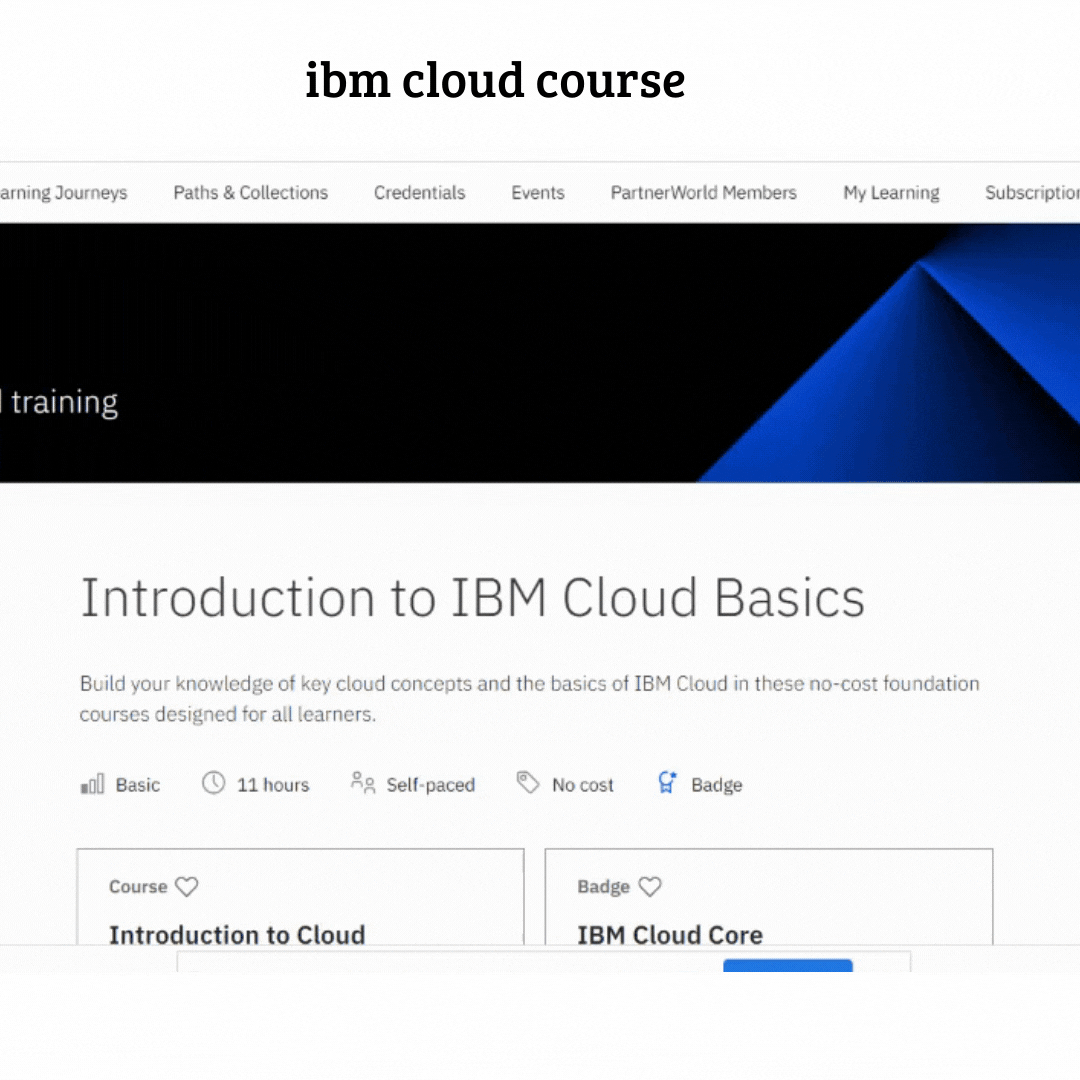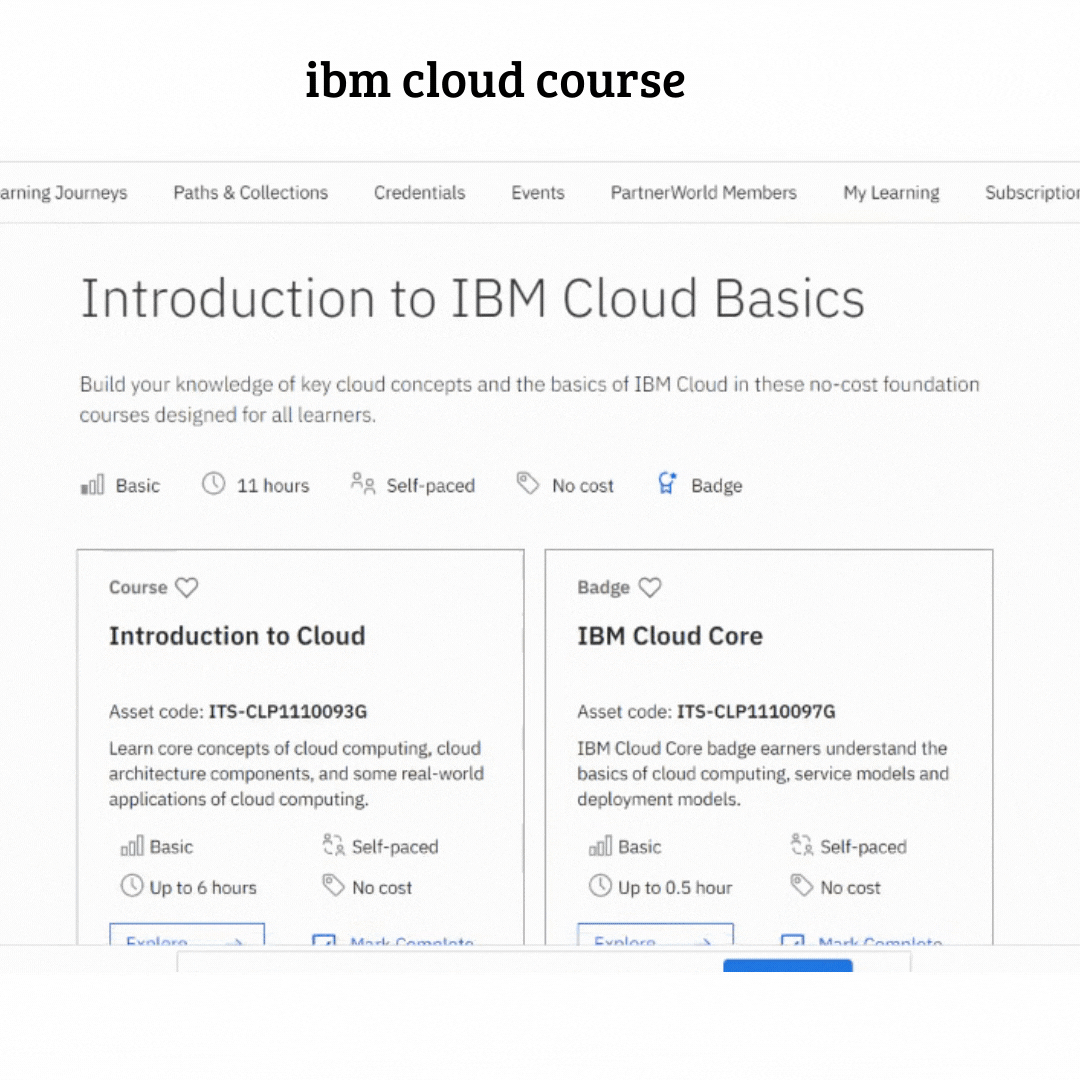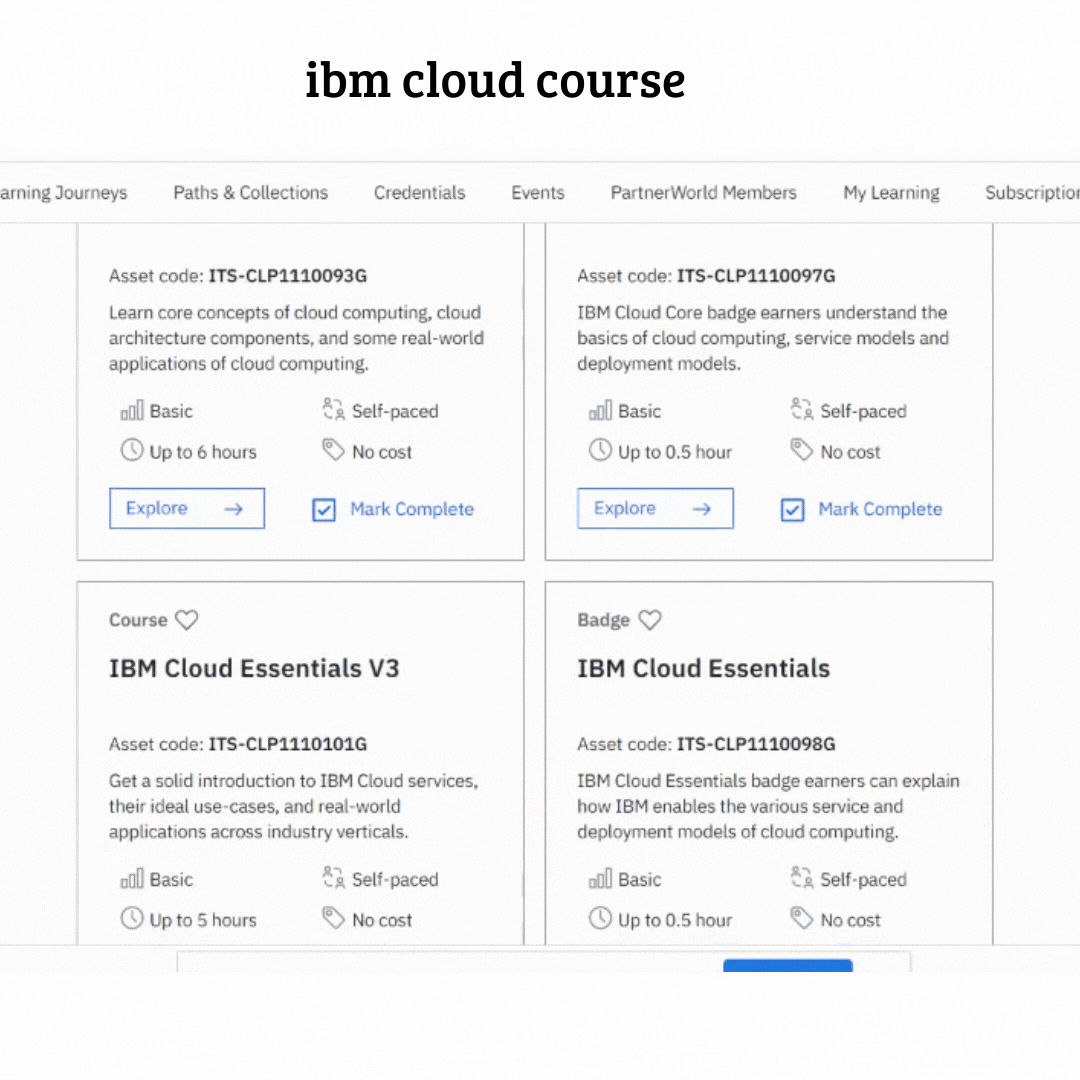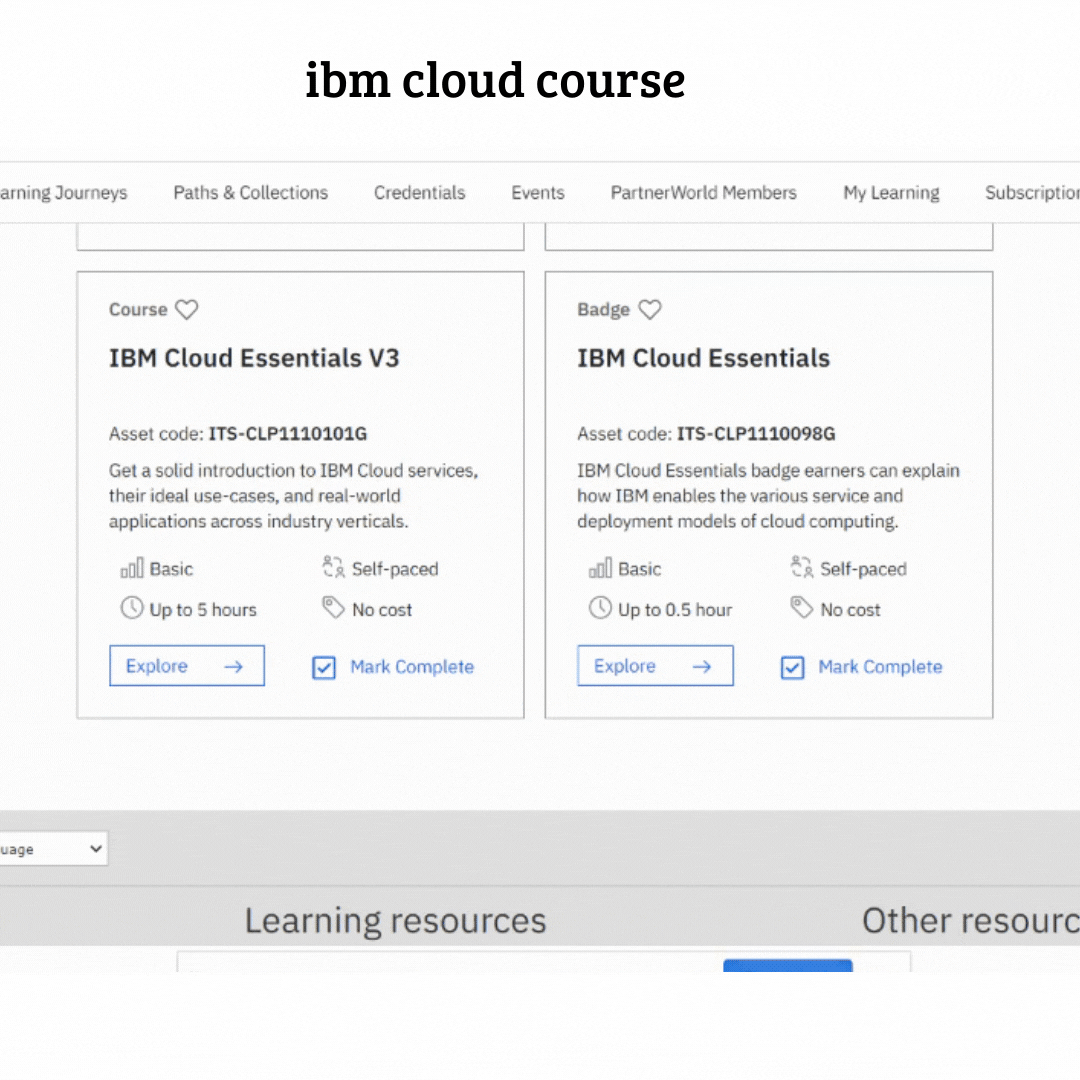
IBM has announced the launch of the most powerful educational course about cloud computing
this course change my mind as digital services provider learn more
on my personal feedpack to the introduction course it is easy to understand and it is explained professionaly
the introduction course is diveded into seven modules (i will explain in detail all these modules later )
The minimum passing mark for the course is 70% with the following weights:
50% - All Graded Quiz Questions
50% - The Final Exam
Though Graded Quiz Questions and the Final Exam have a passing mark of 50% each, the only grade that matters is the overall grade for the course.
Graded Quiz Questions have no time limit. You are encouraged to review the course material to find the answers as this counts for 50% of your mark.
The final exam has a 1-hour time limit.
Attempts are per question in both, the Review Questions and the Final Exam:
One attempt - For True/False questions
Two attempts - For any question other than True/False
and after pssing the exame successfully you will take certification like that:
According to an IBM Institute for Business Value study, more than three-quarters of enterprises today are using cloud computing to expand into new industries. 74% have adopted cloud to improve customer experience; and 71% use cloud to create enhanced
It is a revolution in that it has changed the way the world consumes compute services by making them more cost-efficient while also making organizations more agile in responding to changes in their markets.
for whom this course ?
Anyone and everyone who wants to learn about Cloud Computing - whether you want to just understand what is Cloud (e.g. C-level execs, Managers, Sellers, Students, etc.) or start a career as a Cloud Practitioner (e.g. Developers, Systems/Cloud Architects, Technical Leads, Data Engineers, Security Engineers, Consultants, Technical Sellers, etc.)
What will you learn in this course?
- module 1:overview of cloud computing
- what is the cloud ?
- define the charactarists of cloud
- Define the cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- You will become familiar with some key cloud service providers and the services they offer
- you will learn how to create an account on a public cloud platform IBM cloud.
- module 2:Cloud Adoption and Emerging Technologies
- case studies
- the emerging technologies that are availableon the cloud
- module 3: cloud computing service and deployment models
- infrastructure as a service (IAAS)
- platform as a service (PAAS)
- Software as a service (SAAS)
- public cloud
- private cloud
- hypird cloud
- Module 4 - Components of Cloud Computing
- Module Introduction and Objectives
- Overview of Cloud Infrastructure
- Virtualization and Virtual Machines Explained
- Types of Virtual Machines
- Bare Metal Servers
- secure Networking in Cloud
- Containers
-
Module 5 - Cloud Computing Storage and Content Delivery Networks
- Basics of Cloud Storage
- File Storage
- Block Storage
- Object Storage Overview
- Object Storage - Tiers and APIs
- Content Delivery Networks
- Hands-on Lab: Create an Object Storage Instance and add items
- Module 6 - Emergent Trends, Cloud Native, DevOps and Application Modernization
- Hybrid Multicloud
- >Microservices
- Serverless Computing
- Cloud Native Applications
- DevOps on the Cloud
- Application Modernization
- [Optional] Bonus Module 7 - Cloud Security, Case Studies and Jobs in Cloud Computing
- What is Cloud Security - Part 1
- What is Cloud Security - Part 2
- Case Studies in Different Industry Verticals
- Career Opportunities and Job Roles in Cloud Computing
module one:overview of cloud computing
what is the cloud computing ?
NIST defines cloud computing as a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
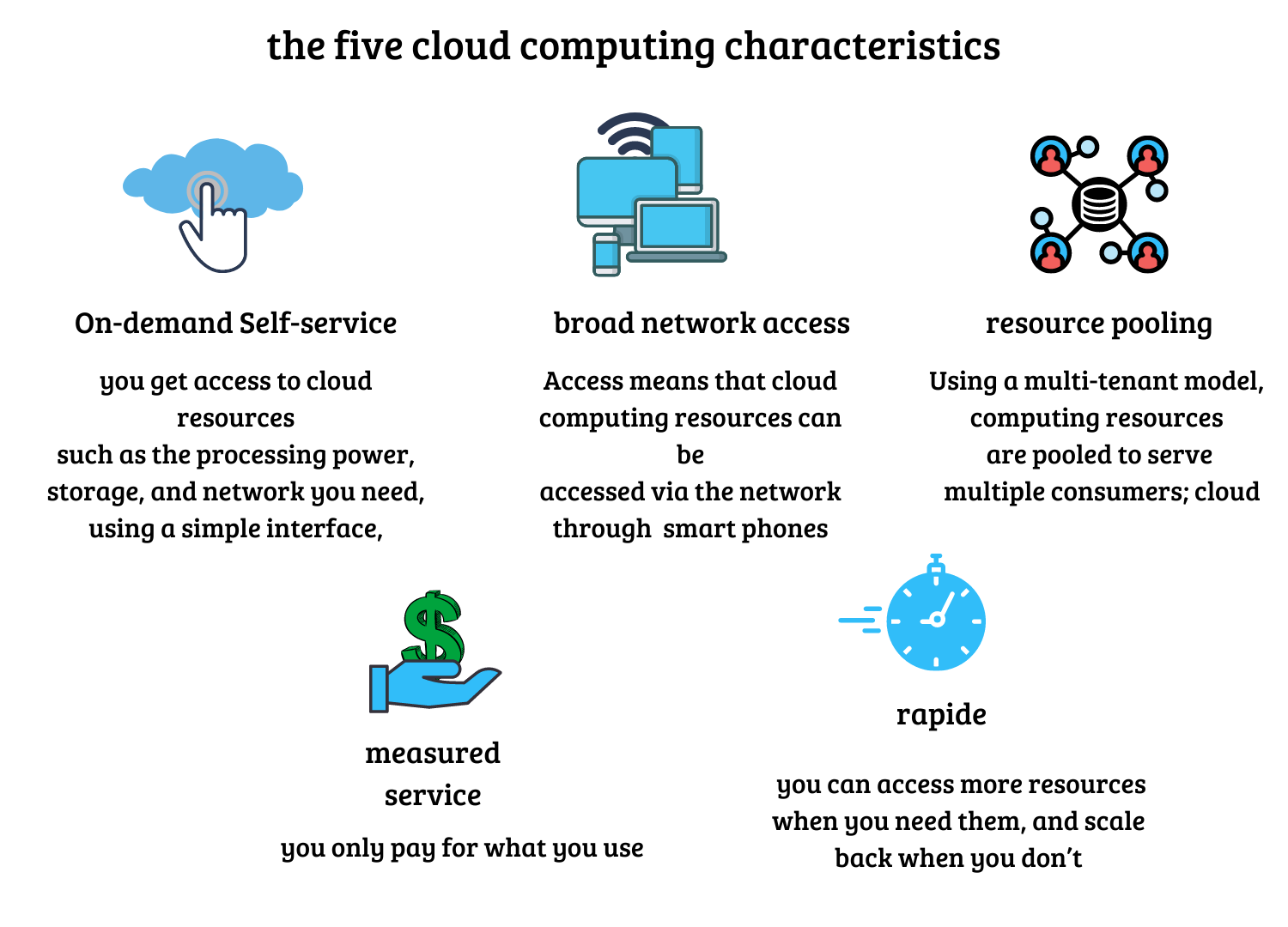
This cloud computing is composed of five essential characteristics which are included in three service models.
cloud computing characteristics are :
cloud computing service models are:
Cloud computing allows us to utilize technology as a service, leveraging remote resources on-demand, on a pay-as-you-model. There are three main service models available on the cloud—Infrastructure-as-a-Service, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
cloud computing deployment models are:
Deployment models indicate where the infrastructure resides, who owns and manages it, and how cloud resources and services are made available to users. There are three main deployment models available on the cloud—Public, Private, and Hybrid.
what about IBM cloud ?
The IBM cloud platform globally deployed across data centers around the world, combines platform as a service (PaaS) with infrastructure as a service (IaaS) to provide an integrated experience. The platform scales and supports both small development teams and organizations, and large enterprise businesses. The platform is built to support your needs whether it's working only in the public cloud or taking advantage of a multicloud deployment model. IBM Cloud offers a variety of services including Compute, Network, Storage, Management, Security, Databases, Analytics, AI and Cloud Paks.

Lab Instructions:
You will perform this lab by completing the following tasks:
- Sign-up
- Confirm
- Login
module two:Cloud Adoption and Emerging Technologies
case studies
we will look at how some of the leading businesses have transformed the way they work to provide better customer service, remove barriers to innovation, achieve enterprisescale, and accelerate growth, using cloud technologies.

UBank launched new initiatives in an IBM Cloud Platform environment, including a virtual assistant that incorporates IBM Watson technology to support the bank’s online home loan application. The results: Faster time to market made possible through the Cloud Platform framework that streamlines development and empowers product teams.

Bitly has journeyed from a startup that offered intelligent link-shortening technology adopted by users to compress lengthy URLs for social media posts, to an enterprise product. Seeking an agile, cost-effective IT infrastructure to support this transition, Bitly started planning for cloud migration. Their need was to have a cloud-based model with pay-as-you-go pricing, the ability to scale up and scale down, a more global presence, and the ability to geodistribute into more POPs. And they wanted it to be low-risk. Bitly migrated to an IBM Cloud environment, establishing a scalable hosting platform for low-latency delivery to enterprise customers around the world. The results: 25 billion data-infused links migrated from one hosting site to Cloud infrastructure with data center locations worldwide. 1 billion user interaction data set stored and managed in a flexible, cost-effective

Financial traders demand extreme speed and availability from trading systems. Profitability depends on split-second decisions. As a leading online broker in forex, commodities, equities, cryptocurrencies, indices, and other financial instruments, ActivTrades enables investors to buy and sell on numerous financial markets. Investors need reliable access to accurate market information, combined with the ability to move rapidly to execute trades. As its client base grew, ActivTrades wanted to cut latency, accelerate execution, and streamline the delivery of new functions. ActivTrades migrated three major trading systems from on-premises infrastructure to IBM Cloud for VMware solutions, backed by data storage, networking, and security offerings on the IBM Cloud. The results: Up to 3X performance boost, helping clients seize fleeting opportunities for profit. Security-rich cloud platform with ultra-high availability protects client investments. Hours, not days to fire up new resources, for faster response to emerging requirements.
the emerging technologies that are available on the cloud
Artificial Intelligence or AI, internet of things or IoT, and Cloud
There is a three-way relationship between Artificial Intelligence or AI, internet of things or IoT, and Cloud.
IoT delivers the data, AI powers the insights, and both these emerging technologies leverage
cloud’s scalability and processing power to provide value to individuals and businesses
alike.
Blockchain and Analytics on the Cloud
Blockchain is transactional applications. It is an immutable Network allowing members to view only those transactions that are relevant to them. The more open, diverse, and distributed the network, the stronger the trust and transparency in the data and transactions. 85% of businesses today rely on multiple clouds to meet their IT
module three: cloud computing service and deployment models
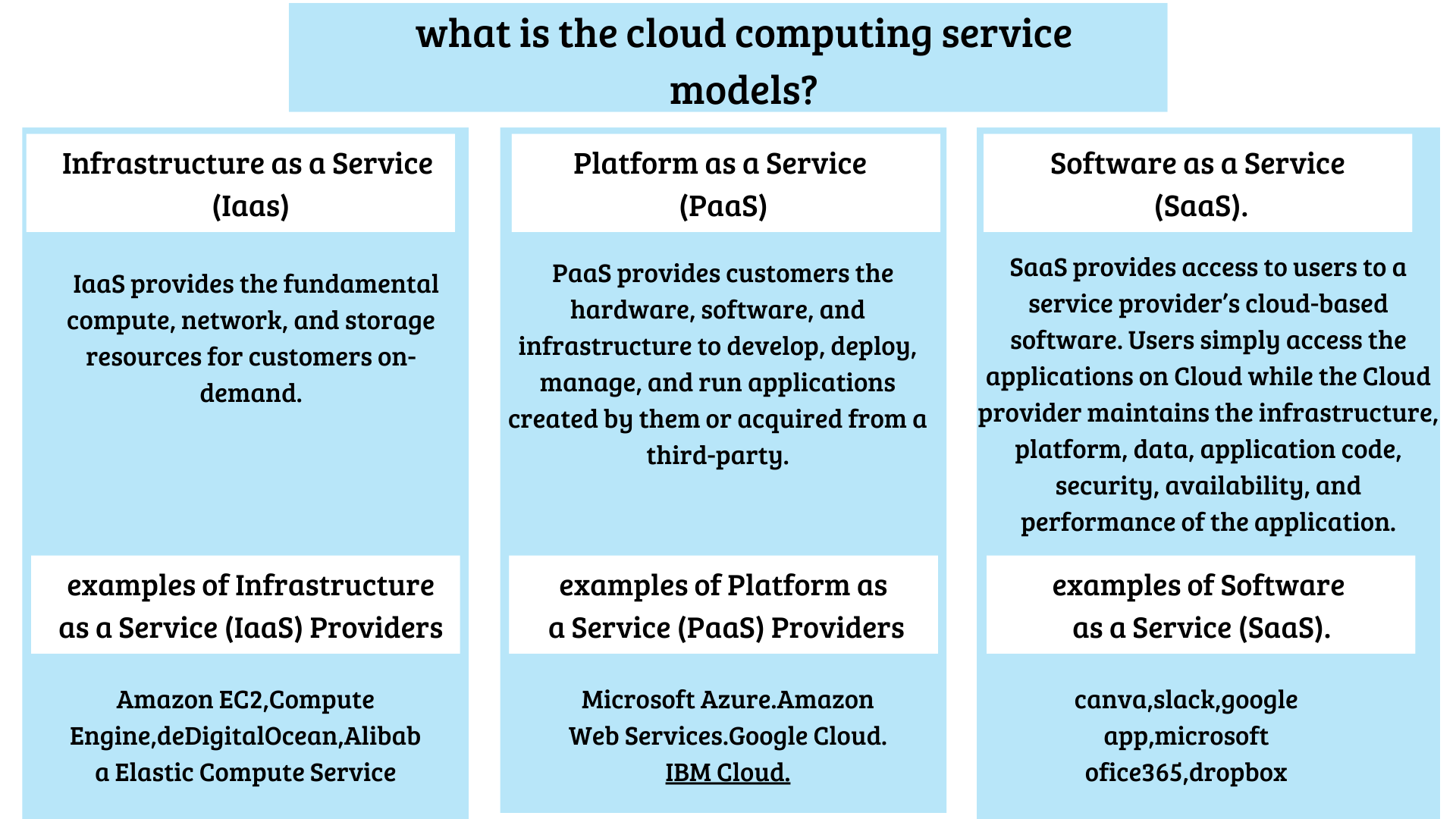
cloud computing service models are:
Cloud computing allows us to utilize technology as a service, leveraging remote resources on-demand, on a pay-as-you-model. There are three main service models available on the cloud—Infrastructure-as-a-Service, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
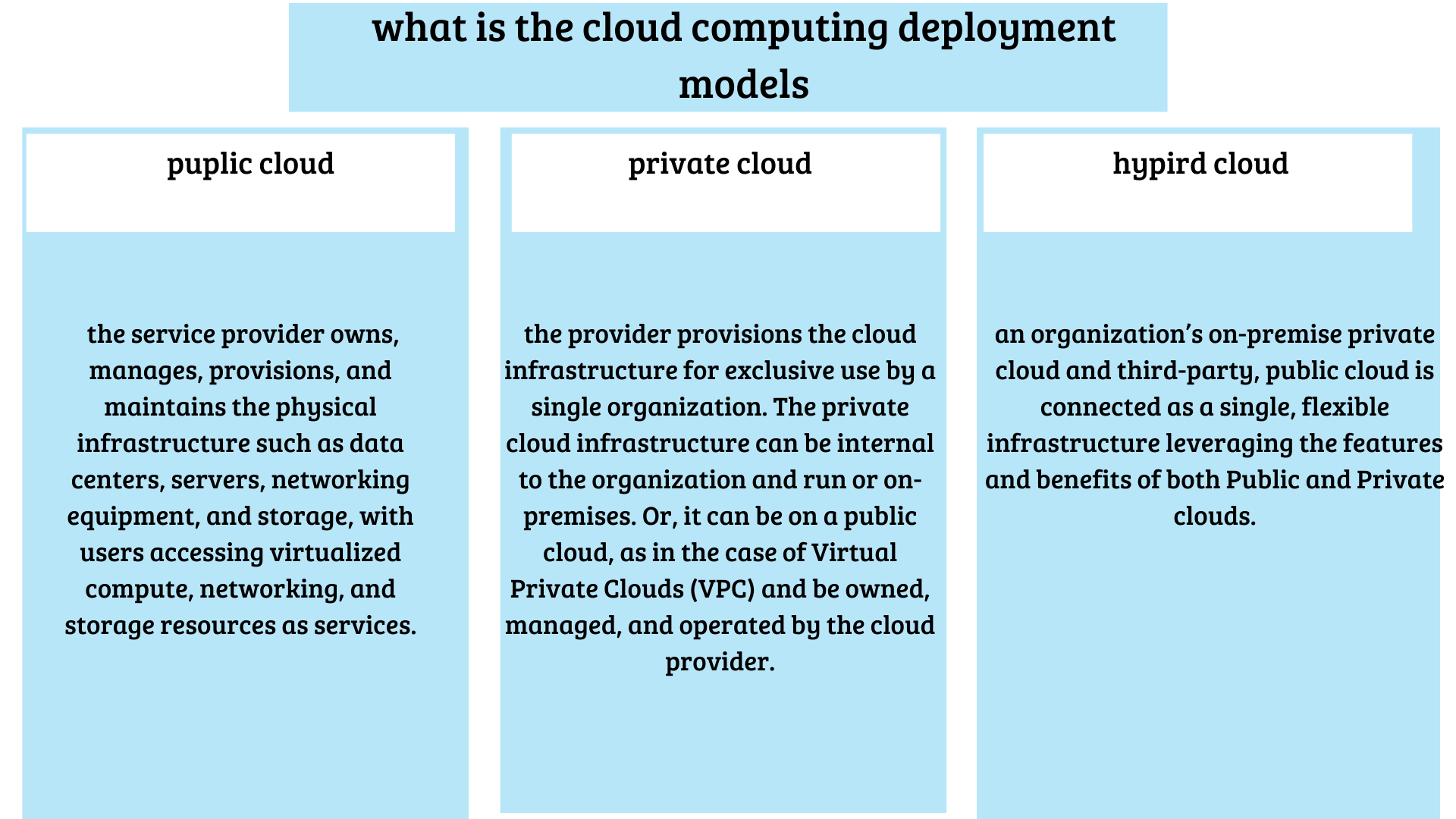
cloud computing deployment models are:
Deployment models indicate where the infrastructure resides, who owns and manages it, and how cloud resources and services are made available to users. There are three main deployment models available on the cloud—Public, Private, and Hybrid.

Module 4 - Components of Cloud Computing
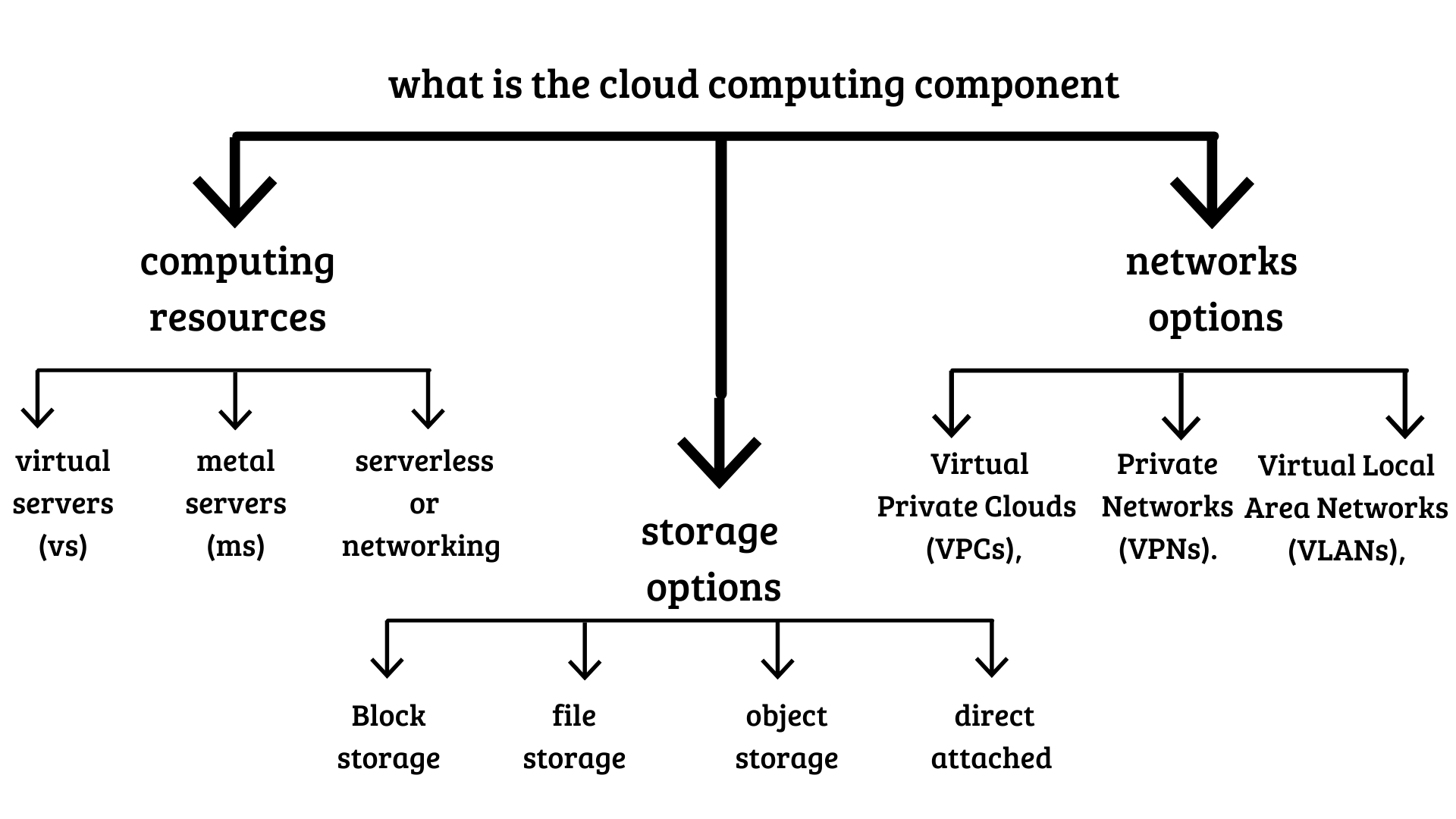
A cloud Data center is a huge room or a warehouse containing cloud infrastructure. These data centers contain pods and racks or standardized containers of computing resources such as servers, as well as storage, and networking equipment Computing Resources: Cloud providers offer several compute options – Virtual Servers, Bare Metal Servers, and “Serverless” computing resources.
virtual servers (VMs)
What makes a VM or Vs? A VM is simply a software-based computer. They're run like a physical computer. They have an operating system and applications, and they're completely independent of one another, but you can run multiple of them on a hypervisor. And the hypervisor manages the resources that are allocated to these virtual environments from the physical server. Because they're independent you can run different operating systems on different virtual machines. You could run Windows here, or Linux here, or UNIX here for example. So once you have your hypervisor installed, you can build virtual environments, or virtual machines, What a hypervisor is, it's simply a piece of software that runs above the physical server, or host.they do is essentially pull the resources from the physical server and allocate them to your virtual examples would be VMware, ESXi, or Microsoft Hyper-v, or even open-source, or Oracle, VirtualBox
metal servers
it's dedicated to a single customer. The cloud provider actually takes the physical server and plugs it into a rack in a data center for customers. The cloud provider manages the server up to the operating system (OS), which means if anything goes wrong with the hardware or rack connection, they will fix or replace it and then reboot the server. The customer is responsible for administering and managing everything else on the server. Bare metal servers are either preconfigured by the cloud provider to meet workload packages or they can be custom-configured as per customer specifications. This includes the processors, RAM, hard drives, specialized components, and the OS. Customers can also install their own OS and can install certain hypervisors that aren't available from the cloud provider, and thus create their own virtual machines and farms. With bare metal servers you can also add GPUs, which are designed for accelerating scientific computation, data analytics
serverless or networking
The main difference stems from the fact, that in the cloud, we use logical instances of networking elements as opposed to physical devices. To create a network in the cloud, one starts by defining the size of the network, or the IP address range that establishes the boundaries or the cloud network. Cloud networks are deployed in networking spaces that are logically separated segments of the networks using options, including Virtual private Cloud (VPC) that in turn can be divided into smaller segments called subnets. Logically segmented cloud networks are private carveout of the cloud that offer customers the security of private clouds and the scalability of public clouds. Cloud resources, such as VMs or Virtual Server Instances (VSIs), Storage, network connectivity and load balancers are deployed into subnets. Using subnets allows users to deploy enterprise applications using the same multi-tier concepts used in on-premises environments. Subnets are also the main area where security is implemented in the cloud. Every subnet is protected by Access Control Lists (ACLS) that serve as a subnet-level fire wall. Within the subnet, one could create Security Groups that provide security at the instance level such as VSIs. Once you build a subnet, then it is time to add some VSIs and storage
serverless computing
The serverless model requires no provisioning of servers, installation of application stacks and software, or operation of the infrastructure by the developer. Serverless computing runs code only on-demand on a per-request basis, scaling transparently with the number of requests being served. Serverless enables end users to pay only for resources being used, never paying for idle capacity, which is unlike virtual servers on the cloud—where end users pay for VMs as long as they are running even if idle. Effectively, serverless abstracts the infrastructure away from developers. Code is executed as individual functions where each function runs inside a stateless container. No prior execution context is required to serve a request; and with each new request, a new instance of the function is invoked.
Module 5 - Cloud Computing Storage and Content Delivery Networks
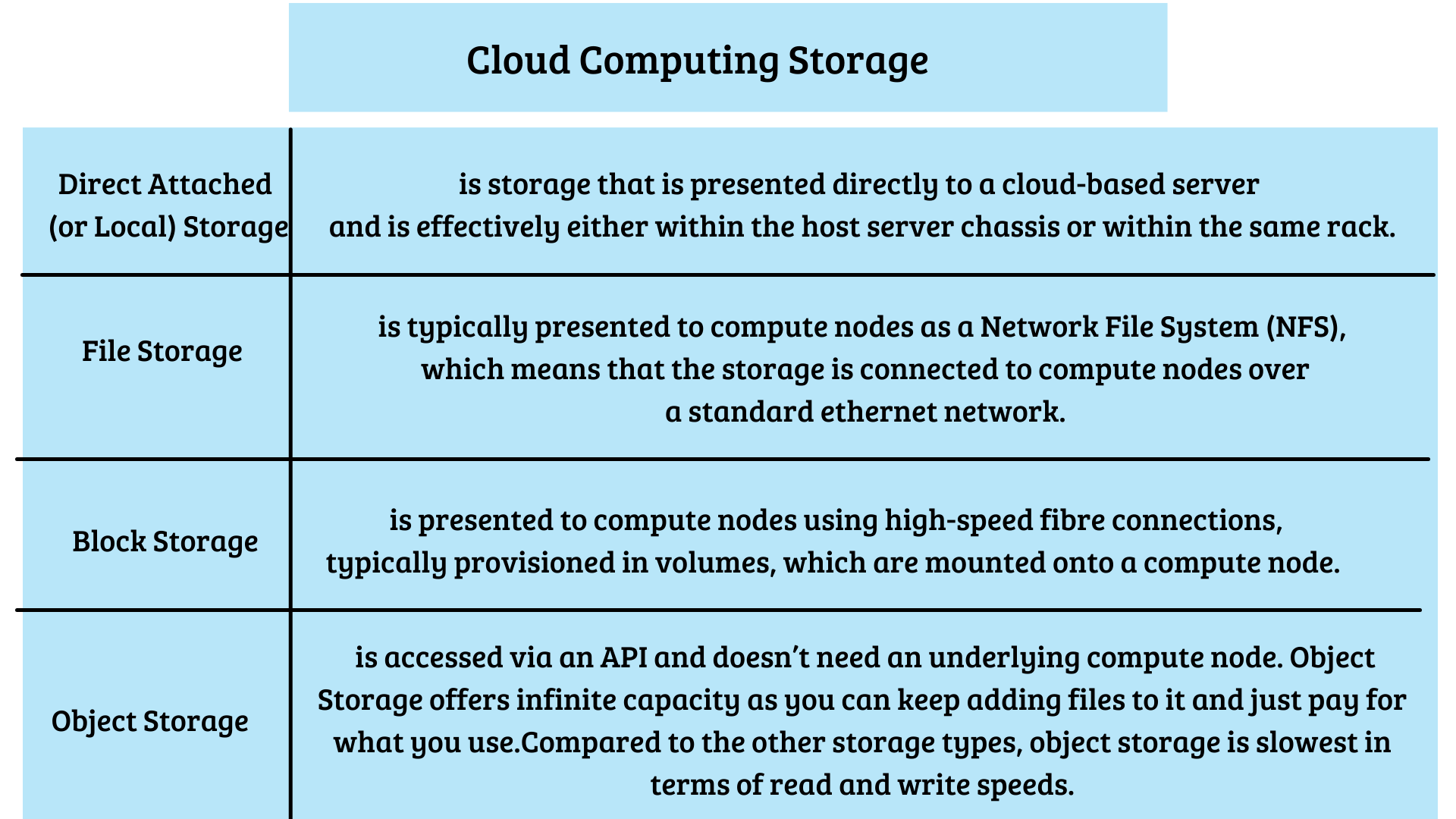
Cloud Computing Storage
Cloud storage is where you save data and files in the cloud. Certain storage must be attached to a compute node before the storage can be accessed, whereas other storage types can be directly accessed either through the public Internet or a dedicated private network connection. Cloud providers host, secure, manage, and maintain the cloud storage and associated infrastructure to ensure you have access to your data when you need it. Cloud storage services allow you to scale your capacity as you need so you only pay for what you provision, usually on a ‘per gigabyte’ basis. The cost of storage will vary by type but in general, the faster the read / write speed of the storage, the higher the per gigabyte cost.there are the four main types of cloud storage - Direct Attached, File, Block, and Object Storage
Content Delivery Networks
A content delivery network, or CDN, is a distributed server network that delivers temporarily stored, or cached, copies of website content to users, based on the user's geographic location. A CDN stores this content in distributed locations and reduces the distance between your website visitors, and your website server.
Module 6 - Emergent Trends, Cloud Native, DevOps and Application Modernization
● Hybrid Multicloud is a cloud adoption strategy that makes it possible for public clouds, private clouds, and on-premises IT to interoperate seamlessly while leveraging the best cloud-based services from different public cloud providers.
the key elements of a hybrid Multicloud strategy are
Connects an organization’s on-premise private cloud and third-party public cloud into a single infrastructure
● Microservices architecture is an approach in which an application is built as a collection of loosely coupled and independently deployable components or services, leading to efficient development, maintenance, and upgradation cycles.
● Serverless Computing is an approach to computing that offloads responsibility for common infrastructure management tasks for application runtimes to cloud providers, allowing developers to focus their time and effort on development and testing, and not have to worry about provisioning, maintaining and scaling compute resources.
● Cloud native applications are applications that are built or refactored to work in the cloud environment. These applications, developed using DevOps methodologies, consist of microservices packaged in containers that can run in any environment—making it possible to create and update features in quick iterative cycles.
● DevOps is a collaborative approach that enables development and operations teams to continuously deliver software in quick iterative cycles while reducing overhead, duplication, and rework. DevOps’ tools, practices, and processes help tackle the complexities and challenges posed by the cloud, allowing solutions to be delivered and updated —quickly and reliably.
● Application Modernization helps organizations accelerate their digital transformation, take advantage of new technologies and services, and become more responsive to changing market dynamics. Cloud computing is one of the key enablers of application modernization.

